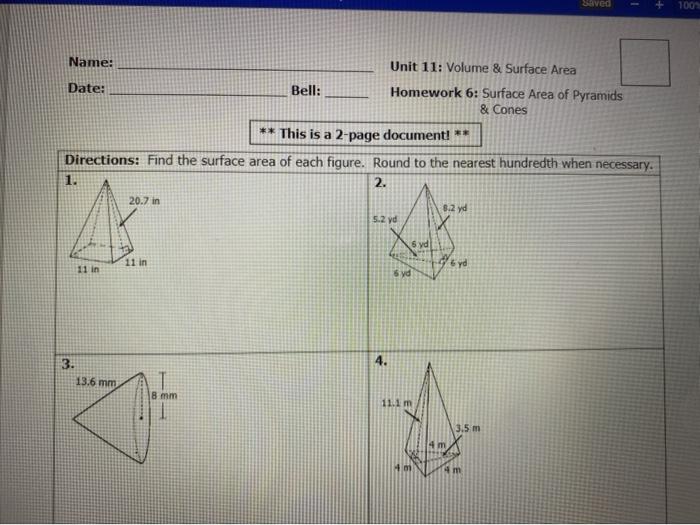
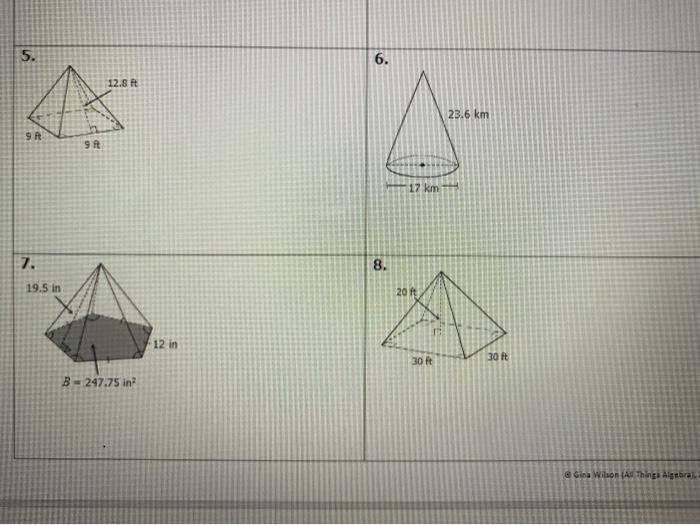
Homework 6 surface area of pyramids and cones – Homework 6: Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones embarks on an illuminating journey into the realm of geometry, unraveling the intricacies of calculating surface areas for these fascinating three-dimensional shapes.
Delving into the concepts of pyramids and cones, we will uncover the formulas that govern their surface areas, unraveling the relationship between their dimensions and the extent of their surfaces.
Surface Area of Pyramids: Homework 6 Surface Area Of Pyramids And Cones
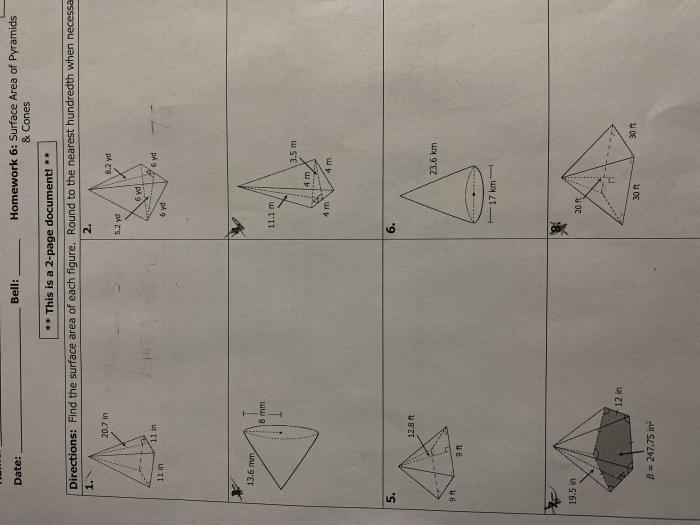
The surface area of a pyramid is the sum of the areas of its faces. For a regular pyramid, all faces are congruent triangles. The formula for the surface area of a regular pyramid is:
S = (1/2)P x l + B
where:
- S is the surface area
- P is the perimeter of the base
- l is the slant height (the height of the triangle faces)
- B is the area of the base
Examples of Surface Area of Pyramids, Homework 6 surface area of pyramids and cones
To calculate the surface area of a square pyramid with a base length of 10 cm and a slant height of 15 cm, we can use the formula:
S = (1/2)P x l + B
The perimeter of the base is 4 x 10 cm = 40 cm.
The area of the base is 10 cm x 10 cm = 100 cm 2.
The surface area is (1/2) x 40 cm x 15 cm + 100 cm 2= 300 cm 2.
Surface Area of Cones
The surface area of a cone is the sum of the areas of its base and its lateral surface. The lateral surface is the surface area of the cone’s sides.
The formula for the surface area of a cone is:
S = πr2+ πrl
where:
- S is the surface area
- π is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the radius of the base
- l is the slant height
Examples of Surface Area of Cones
To calculate the surface area of a cone with a base radius of 5 cm and a slant height of 10 cm, we can use the formula:
S = πr2+ πrl
The surface area is π x 5 cm 2+ π x 5 cm x 10 cm = 78.54 cm 2.
Comparing Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones
The surface area formulas for pyramids and cones are similar in that they both involve the area of the base and the slant height. However, the formula for the surface area of a cone includes an additional term for the lateral surface area.
The shape of the base also affects the surface area. Pyramids have polygonal bases, while cones have circular bases. This difference in base shape leads to different formulas for the area of the base.
Applications of Surface Area Calculations
Surface area calculations are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Architecture: Surface area calculations are used to determine the amount of paint or other materials needed to cover a building.
- Engineering: Surface area calculations are used to determine the heat transfer rate of a heat exchanger.
- Design: Surface area calculations are used to determine the size of a solar panel or other device that needs to absorb or emit heat.
Questions and Answers
What is the formula for calculating the surface area of a pyramid?
The surface area of a pyramid is given by the formula: Surface Area = Base Area + (1/2) – Perimeter of Base – Slant Height
How can I apply the formula to different types of cones?
To calculate the surface area of different types of cones, simply substitute the appropriate values for the radius of the base and the slant height into the formula: Surface Area = πr² + πrl