Monolingual ap human geography definition – Monolingualism in human geography refers to the phenomenon of individuals or communities using only one language in their daily lives. This concept holds significant implications for communication, education, and cultural diversity, making it a topic worthy of exploration.
Monolingualism stands in contrast to multilingualism, where individuals are proficient in multiple languages. Understanding the causes and consequences of monolingualism helps us appreciate the complexities of linguistic landscapes and their impact on societies.
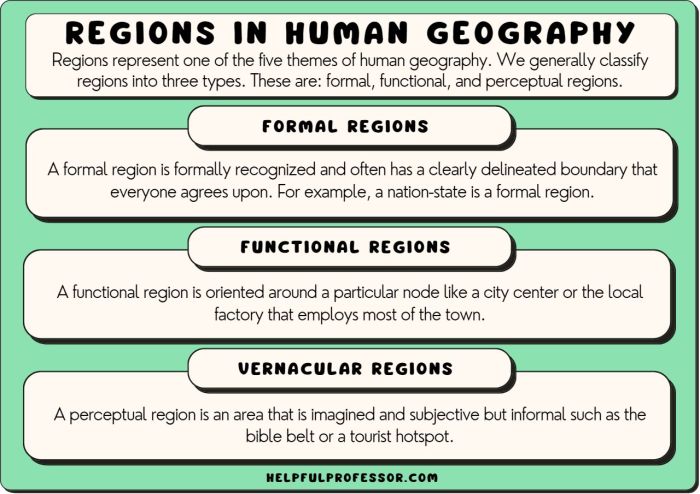
Definition of Monolingualism in Human Geography: Monolingual Ap Human Geography Definition
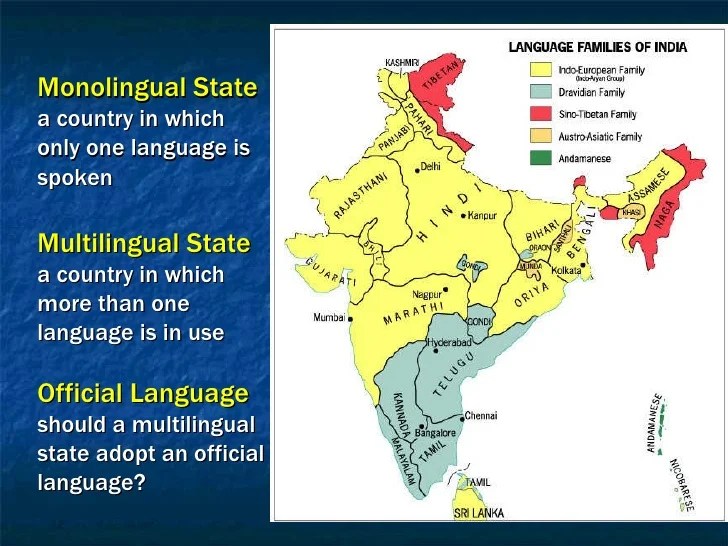
Monolingualism in human geography refers to the exclusive use of a single language by an individual or a community within a specific geographic area. It contrasts with multilingualism, where multiple languages are used within a given region.
Causes and Factors of Monolingualism
The causes of monolingualism vary widely and can be attributed to historical, cultural, and socio-economic factors. Historical events, such as colonization and migration, have played a significant role in shaping language distribution and usage.
Cultural factors, including cultural identity, language preservation, and education policies, can also influence monolingualism. Socio-economic factors, such as access to education, employment opportunities, and social mobility, can further contribute to the prevalence of monolingualism in certain regions.
Spatial Distribution of Monolingualism
The spatial distribution of monolingualism is not uniform across the globe. Regions with high levels of monolingualism are often found in isolated areas, such as remote islands or mountainous regions, where contact with other linguistic communities is limited.
Conversely, regions with high levels of multilingualism are often found in areas with diverse populations, such as urban centers and border regions, where individuals are exposed to multiple languages from an early age.
Consequences of Monolingualism, Monolingual ap human geography definition
Monolingualism can have both positive and negative consequences for individuals, communities, and societies.
On the positive side, monolingualism can foster a strong sense of cultural identity and community cohesion. It can also facilitate communication within a specific group and reduce the potential for misunderstandings.
However, monolingualism can also limit an individual’s ability to communicate with people from other linguistic backgrounds, which can hinder social interaction, educational opportunities, and employment prospects.
Strategies to Promote Multilingualism
Promoting multilingualism in monolingual regions requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both individual and societal factors.
Effective strategies include:
- Encouraging early childhood language exposure through immersion programs and bilingual education.
- Providing accessible language learning opportunities for adults through community-based programs and online resources.
- Creating supportive policies that promote multilingualism in education, employment, and public services.
- Raising awareness about the benefits of multilingualism and challenging monolingual attitudes.
Future Trends in Monolingualism and Multilingualism
The future of monolingualism and multilingualism is uncertain and subject to ongoing debate. Some experts predict that globalization and increased international travel will lead to a decline in monolingualism and a rise in multilingualism.
Others argue that monolingualism will persist in certain regions due to factors such as cultural preservation and limited access to education. Regardless of the future trends, it is clear that both monolingualism and multilingualism will continue to exist in different parts of the world.
FAQs
What is the main cause of monolingualism?
Monolingualism can arise due to various factors, including limited exposure to other languages, lack of language education, historical isolation, and cultural dominance.
What are the potential consequences of monolingualism?
Monolingualism can limit communication, hinder education, restrict access to information, and potentially contribute to cultural isolation.
How can multilingualism be promoted?
Multilingualism can be fostered through language education programs, language exchange initiatives, and policies that support linguistic diversity.