Faked numbers in tax returns invoices – The manipulation of financial figures in tax returns and invoices, known as “faked numbers,” has emerged as a grave concern, threatening the integrity of financial reporting and eroding trust in the business landscape. This article delves into the far-reaching implications of such fraudulent practices, exploring their impact on financial reporting, detection and prevention mechanisms, legal and ethical ramifications, and consequences for businesses.
The practice of falsifying numbers in tax returns and invoices distorts financial performance, misleads investors and stakeholders, and undermines the reliability of financial statements. This article examines the techniques used to perpetrate such fraud and discusses data analytics and internal controls as effective detection methods.
Furthermore, it highlights the crucial role of auditors in preventing and uncovering these illicit activities.
Impact on Financial Reporting

Faked numbers in tax returns and invoices can have severe consequences for the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. They can distort financial performance, mislead investors and other stakeholders, and undermine the integrity of the financial reporting process.
Misrepresentation of Financial Performance
- Faked numbers can inflate or deflate revenues, expenses, and profits, leading to an inaccurate representation of a company’s financial health.
- This can mislead investors and other stakeholders into making incorrect investment decisions, potentially resulting in financial losses.
Erosion of Trust in Financial Reporting
- Faked numbers undermine the credibility of financial statements and erode trust in the financial reporting process.
- When stakeholders lose confidence in the accuracy and reliability of financial information, it can damage the reputation of companies and the entire financial system.
Detection and Prevention
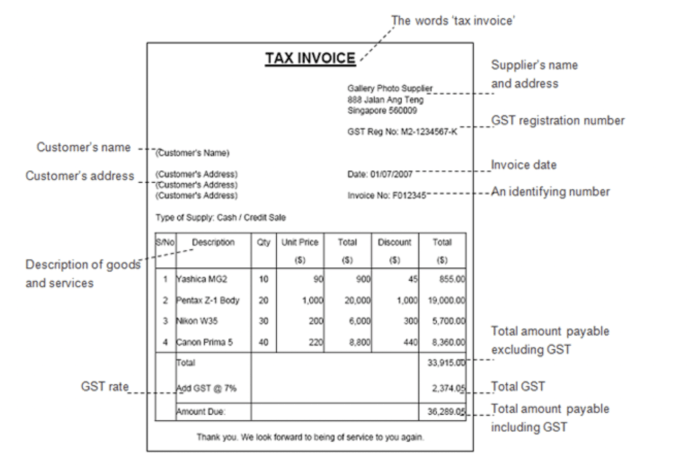
Detecting and preventing the falsification of numbers in tax returns and invoices is crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial reporting. This section examines common methods used to fake numbers, techniques for detection, and the role of auditors in preventing and uncovering such practices.
Common Methods of Faking Numbers
- Overstating Revenues:Inflating sales figures or creating fictitious transactions to increase reported income.
- Understating Expenses:Concealing or omitting expenses to reduce reported expenses and increase profits.
- Manipulating Inventory:Adjusting inventory levels to affect cost of goods sold and reported profits.
- Altering Accounts Receivable:Inflating or deflating accounts receivable to impact revenue recognition and cash flow.
- Fabricating Documents:Creating false invoices, receipts, or bank statements to support faked numbers.
Techniques for Detecting Faked Numbers
Detecting faked numbers requires a combination of data analytics and internal controls. Data analytics techniques include:
- Trend Analysis:Comparing financial data over time to identify unusual fluctuations or inconsistencies.
- Ratio Analysis:Calculating financial ratios to assess the reasonableness of reported numbers.
- Benford’s Law:Analyzing the distribution of digits in financial data to identify anomalies.
Internal controls include:
- Segregation of Duties:Separating tasks related to recording, authorizing, and reconciling financial transactions.
- Reconciliations:Regularly comparing financial records to external sources (e.g., bank statements, vendor invoices).
- Internal Audits:Conducting independent reviews of financial processes and controls.
Role of Auditors
Auditors play a vital role in preventing and detecting faked numbers. Their responsibilities include:
- Assessing Risk:Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of financial misstatement due to faked numbers.
- Performing Substantive Procedures:Conducting tests to verify the accuracy and completeness of financial data.
- Evaluating Internal Controls:Assessing the effectiveness of internal controls in preventing and detecting faked numbers.
- Reporting Findings:Communicating the results of their audit, including any concerns or suspected instances of faked numbers.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Faking numbers in tax returns and invoices carries severe legal and ethical consequences. These actions constitute fraud and tax evasion, which are punishable by law.
Legally, individuals and businesses caught faking numbers face criminal charges, fines, and imprisonment. Tax evasion, in particular, is a serious offense that can result in substantial penalties, including jail time.
Ethical Implications, Faked numbers in tax returns invoices
Beyond the legal repercussions, faking numbers also has significant ethical implications. Such actions undermine the integrity of the tax system and erode public trust in businesses.
When businesses falsify numbers, they gain an unfair advantage over those who comply with the law. This can lead to market distortions and a loss of confidence in the fairness of the economic system.
Examples of Legal Penalties
- In 2021, a company was fined $10 million for intentionally underreporting its income on tax returns.
- In 2019, an individual was sentenced to 5 years in prison for falsifying invoices to evade taxes.
Consequences for Businesses

Faked numbers in tax returns and invoices can have severe consequences for businesses, damaging their reputation, leading to financial losses, and disrupting operations.
Damage to Reputation and Credibility
When businesses are caught using faked numbers, it can seriously damage their reputation and credibility with customers, investors, and stakeholders. This loss of trust can make it difficult to attract new customers, retain existing ones, and secure funding.
Financial Losses
Faked numbers can also lead to significant financial losses. If a business underreports its income, it may face penalties and fines from tax authorities. Additionally, faked numbers can distort financial statements, making it difficult for investors and lenders to make informed decisions.
Operational Disruptions
In some cases, faked numbers can also lead to operational disruptions. For example, if a business overstates its expenses, it may not have enough cash on hand to meet its obligations, leading to delays in payments to suppliers or employees.
Examples of Businesses Affected by Faked Numbers
Several businesses have suffered significant consequences due to faked numbers, including:
- In 2015, Volkswagen was fined $4.3 billion for installing software in its vehicles that allowed them to cheat on emissions tests.
- In 2016, Wells Fargo was fined $185 million for creating millions of unauthorized customer accounts.
- In 2017, Toshiba was forced to restate its financial statements after discovering that it had overstated its profits by $1.2 billion.
Industry Best Practices
To prevent and detect faked numbers in tax returns and invoices, it is essential to implement robust industry best practices. These practices encompass internal controls, data analytics, and ethical corporate culture.
Internal Controls
Internal controls are a crucial component of fraud prevention. They establish clear processes, responsibilities, and segregation of duties to minimize opportunities for manipulation. These controls include:
- Regular reconciliation of accounts
- Independent review of financial statements
- Mandatory vacation time for key personnel
Data Analytics
Data analytics can be a powerful tool for detecting fraudulent activities. By analyzing large volumes of data, anomalies and inconsistencies can be identified that may indicate fraud. Techniques used include:
- Benford’s Law analysis
- Time-series analysis
- Clustering algorithms
Ethical Corporate Culture
An ethical corporate culture is essential for preventing fraud. It promotes integrity, transparency, and accountability throughout the organization. Key elements include:
- Clear code of ethics
- Whistleblower protection policies
- Training and education on fraud prevention
Case Studies
Several companies have successfully implemented effective anti-fraud measures. For example:
- General Electricimplemented a data analytics system that detected a $200 million fraud scheme.
- Citigroupestablished a dedicated fraud prevention team that reduced fraud losses by 50%.
Role of Technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in detecting and preventing faked numbers in tax returns and invoices. Data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain technology have emerged as powerful tools in the fight against fraud.
Data Analytics
Data analytics involves examining large datasets to identify patterns and anomalies. By analyzing invoice and tax return data, algorithms can detect suspicious transactions, such as unusually high or low amounts, inconsistent vendor information, or duplicate invoices.
Artificial Intelligence
AI algorithms can be trained to learn from historical data and identify fraudulent patterns. They can analyze large volumes of data quickly and efficiently, flagging transactions that deviate from expected norms. AI-powered systems can also be used to automate fraud detection processes, reducing the need for manual review.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology provides a secure and immutable record of transactions. By storing invoice and tax return data on a blockchain, businesses can create a tamper-proof audit trail. This makes it difficult for fraudsters to alter or manipulate financial records.
Examples of Technology Solutions
Several technology solutions have been successfully implemented to combat faked numbers in tax returns and invoices. For instance, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) uses a data analytics platform to identify suspicious tax returns. This platform has helped the IRS detect and prevent billions of dollars in fraudulent refunds.
Commonly Asked Questions: Faked Numbers In Tax Returns Invoices
What are the common methods used to fake numbers in tax returns and invoices?
Common methods include overstating revenue, understating expenses, and creating fictitious transactions.
How can businesses prevent faked numbers?
Businesses can implement internal controls, such as segregation of duties, authorization procedures, and regular reconciliations.
What are the legal consequences of faking numbers in tax returns and invoices?
Faking numbers can lead to charges of fraud, tax evasion, and other criminal offenses.